Some call ancient Egypt one the of most influential human civilizations ever. And who can argue with a culture that lasted over 3,000 years! A mark of a great civilization is its cultivation of the arts. And Egyptian pottery was well-cultivated and is a big part of ceramic art history even today.
The Egyptian potter was a celebrated craftsman. In this article, we’ll explore:
- the history of Egyptian ceramics
- how ancient Egyptian pottery was made
- and the significance of what ancient Egyptian potters made
History of pottery in ancient Egypt
Ancient Egypt Periods
Ancient Egypt breaks down into 9 periods and 30 dynasties. Often, Egyptian priests functioned as historians. Of the priests, Manetho wrote The History of Eygpt. This text is used by modern-day scholars to date artifacts and events.

Throughout the article, we’ll reference the 9 periods of Egyptian history. So here’s a list to introduce the periods and give a timeline for what order they happened:
- Old Kingdom
- First Intermediate Period
- Middle Kingdom
- Second Intermediate Period
- Hight Priests (HP) of Amun
- Third Intermediate Period
- Late Period
- Macedonian Period
- Ptolemaic Period
When did Egyptians start making pottery?
Egyptians started making pottery around 4,000 B.C.E. This dates Egyptian pottery earlier than the Old Kingdom.
The earliest Egyptian pottery followed the handbuilding pottery technique. Many of the discovered pieces use the coil handbuilding technique. Decorations were often simple and patterns were commonly geometric designs like the ancient Greeks.
What is Egyptian pottery called?
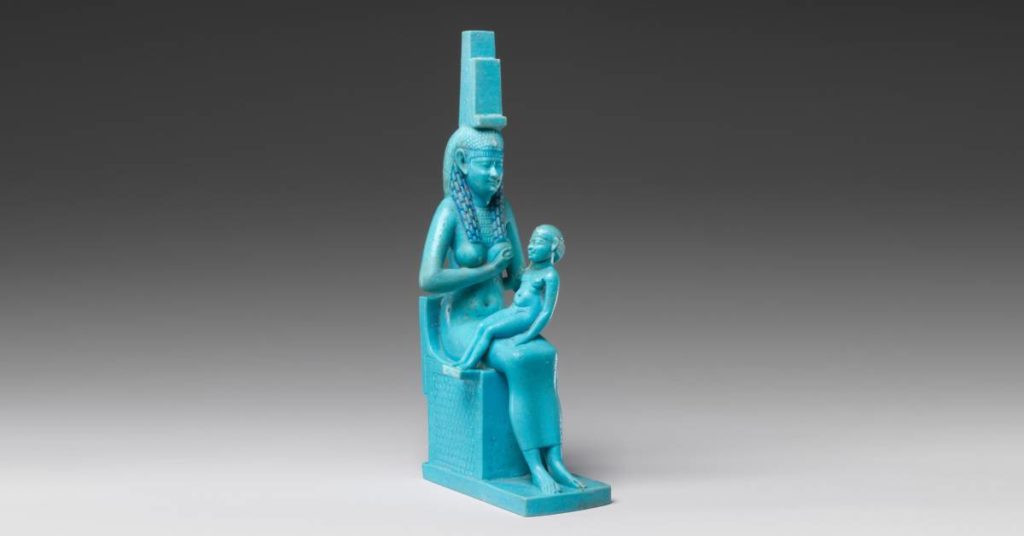
You may see “Egyptian faience” when looking up things about ancient Egyptian pottery. Faience is efflorescence glazing (or self-glazing). Salts in the clay material come to the surface as a clay body drys. A glaze naturally develops when the vessel is fired. Egyptian faience results in bright colors like turquoise or cobalt blue.

Clay used in Egyptian pottery
The two types of clays used for Egyptian pottery are Nile clay and Marl clay. In fact, the types of clay resulted in The Vienna System as a way of classifying wares. The system looks at the size of the organic and non-organic components of the pottery fabric. For Egyptian pottery, there are 10 classifications rooted in the location of where the clay was discovered.
Each year, the Nile flooded bringing with it silt and clay. The material is actually from mountains found in modern-day Ethiopia. Nile clay has high silicon and iron oxide. It typically drys brown and red.
Marl clay is from the desert. It’s often referred to as desert clay. It’s also found along the Nile. It has a yellow or white coloring to it because of limestone deposits.
How did the ancient Egyptians make pottery?
Handbuilding
Early pottery from Eygpt was handbuilt. Handbuilding is a technique of ceramics where one forms clay with hands and simple tools. Egyptian potters used the coil handbuilding technique. In this technique clay rolls (coils) are stacked into the form of a pot.
Decorations on these early clay pots were often simple. Patterns were commonly geometric like the ancient Greeks.
Potter’s wheel in ancient Egypt
Egyptian ceramicists started using the pottery wheel between 2600 B.C.E. and 2500 B.C.E. The time period is considered the “golden age” of the Old Kingdom. The potter wheel allowed for smoother and more uniform finishes leading the way to mass production.
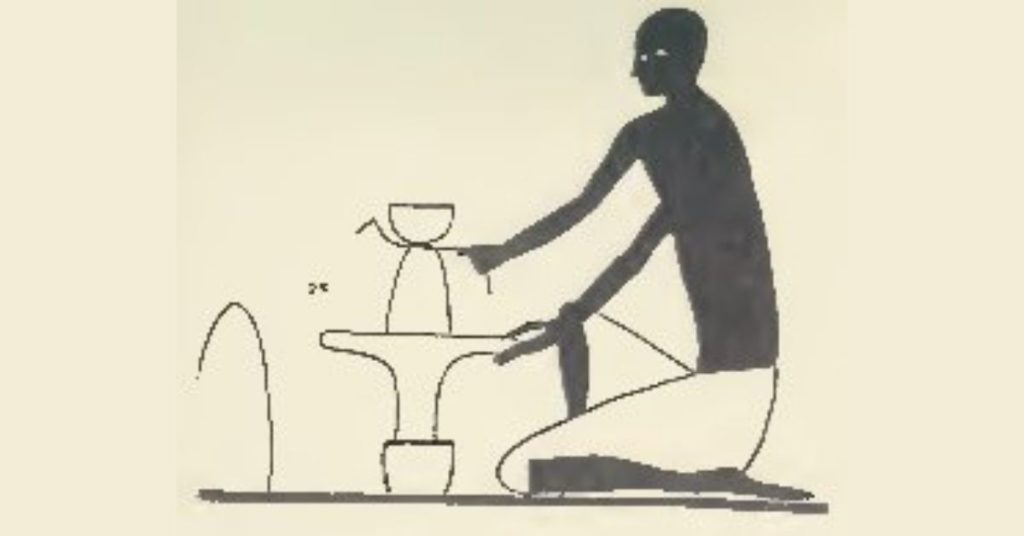
Firing ancient pottery
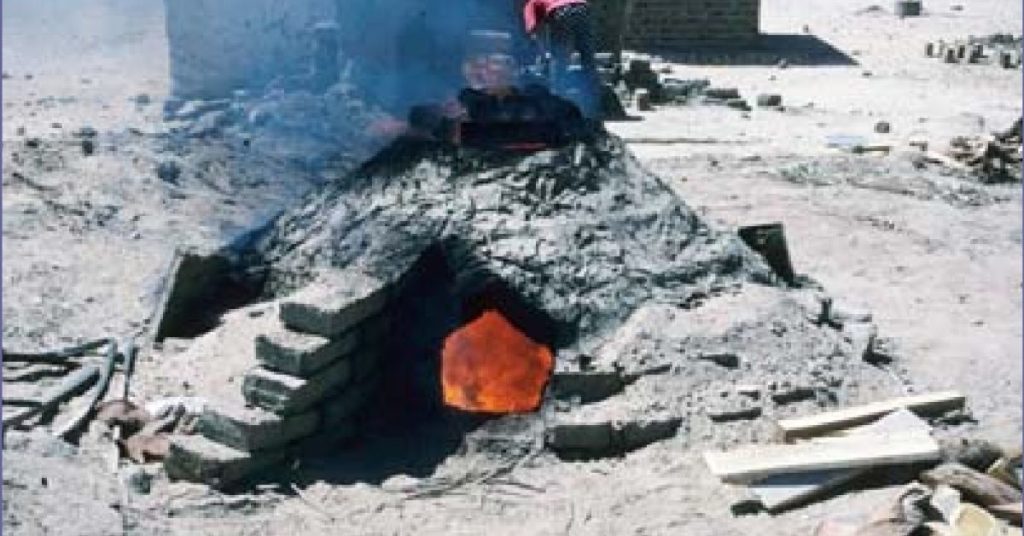
Egyptian potters started with primitive kilns like everyone else in the ancient world.
An early date kiln structure was a pit in the ground. The pottery pieces to be fired stood on blocks and fuel would be underneath. You’d find a “stoke hole” to the side of the kiln to allow the attendant to keep kiln hot. This is a primitive version of an updraft kiln. Here’s a diagram from a study of pottery kilns showing how it would work:
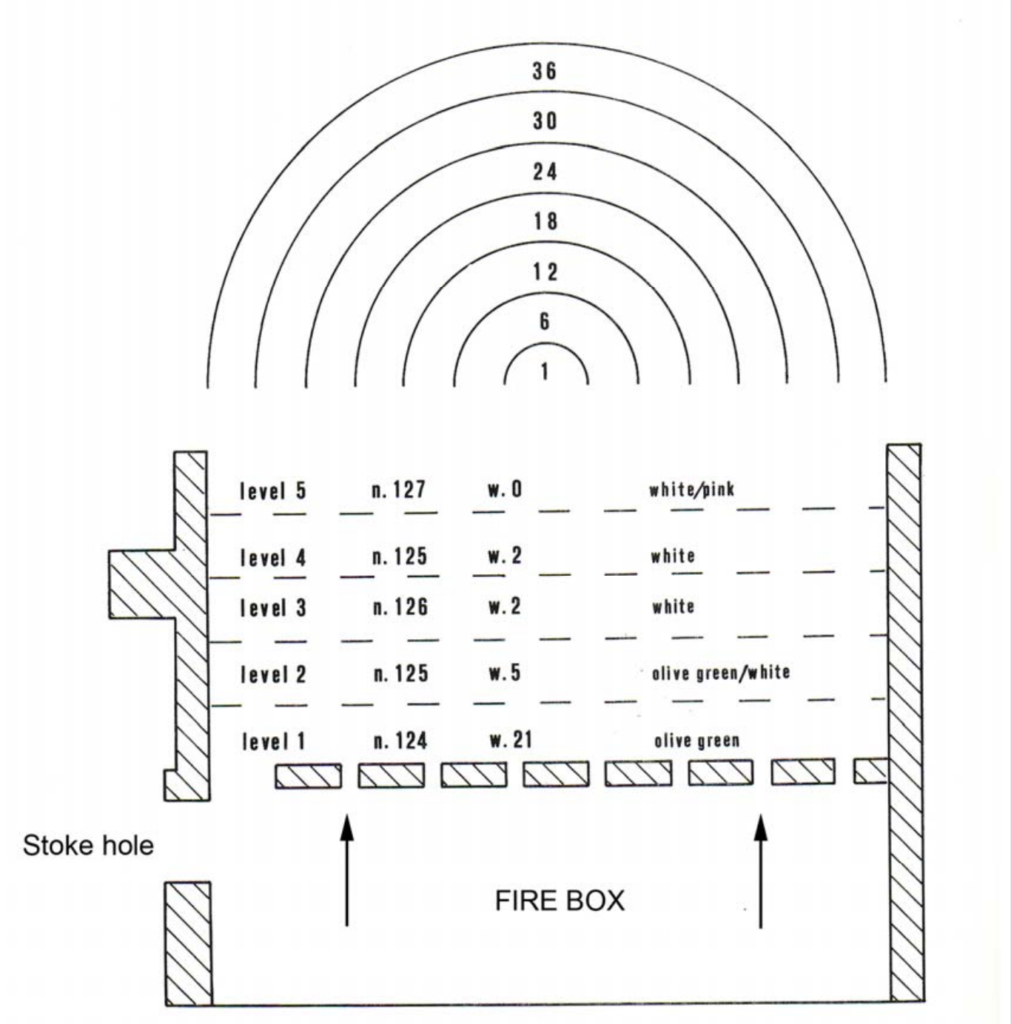
Kiln technology developed allowing for some of the celebrated types of pottery like Faience to come about. Archaeologists often refer to kilns that produced Faience as “furnaces” because of the high temperatures these kilns could reach.

What did ancient Egyptian potters make?
Functional Egyptian Pottery
Ancient Egyptian potters made functional pottery for storing foods or liquids. Other vessels helped complete other daily tasks. Many of the styles of these vessels are like ancient Greek pottery.
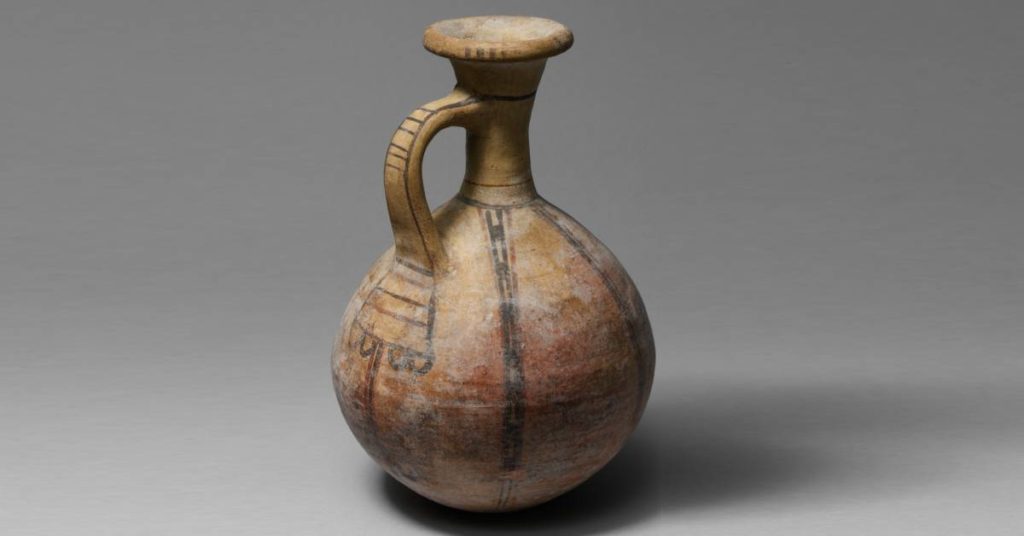
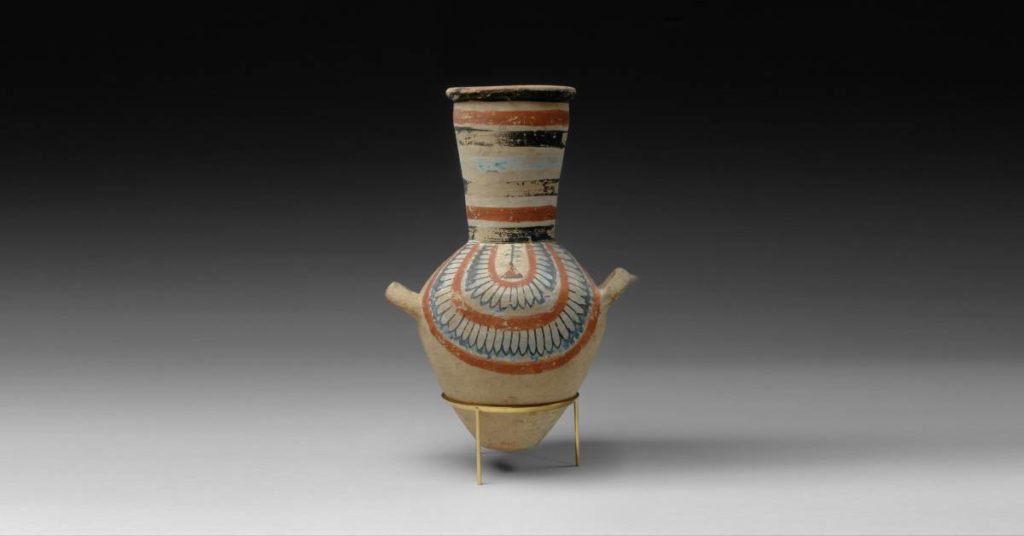


Religious Egyptian Pottery
There’s a deep connection between the Eygptian potter’s art and belief. The god of fertility, Khnum was praised for bringing life. Life in the womb, life to the harvest fields, and life even to other deities. Religious texts gave him titles like “Divine Potter”. It was believed he formed babies from clay, placing them into their mother’s womb.
The parallels of the everyday potter and godly duties’ were intertwined. This plays itself out in the kinds of things ceramicists make.
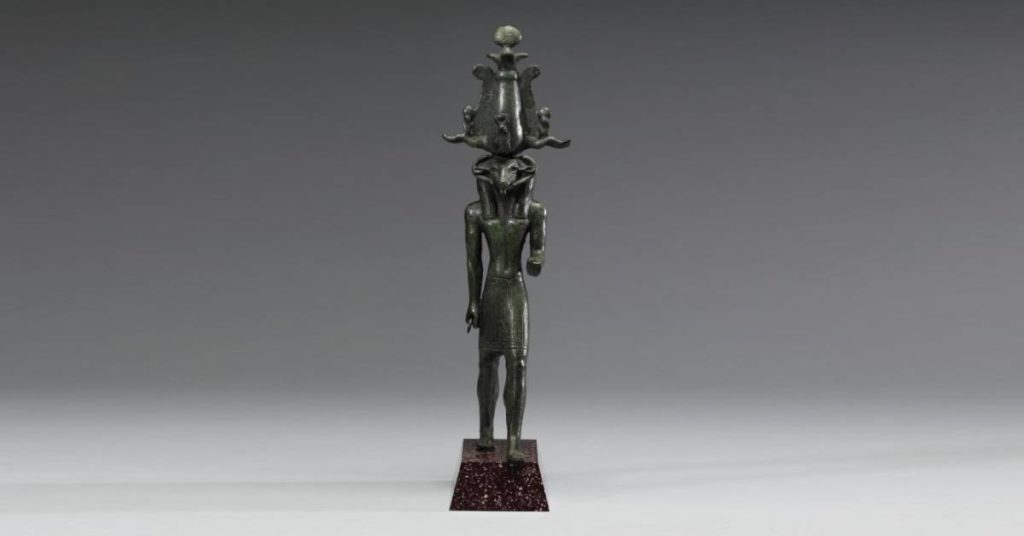

Many Egyptian potters made works for religious ceremonies and had a funerary purpose. These vessels often held oils and fragrant liquids. There were also clay figures and other objects representing Egyptian gods. Many of the beautiful pieces we know from ancient times were used in burials. The tombs of wealthy people and royalty preserved the pottery vessels.
Styles: Pottery in ancient Egypt
Enameled pottery
Enameled pottery is a decoration style that allows the potter to inlay ornamental work. The Egyptians figured out this type of pottery early on. The Egyptians enameled pottery was often blue or blue/green.
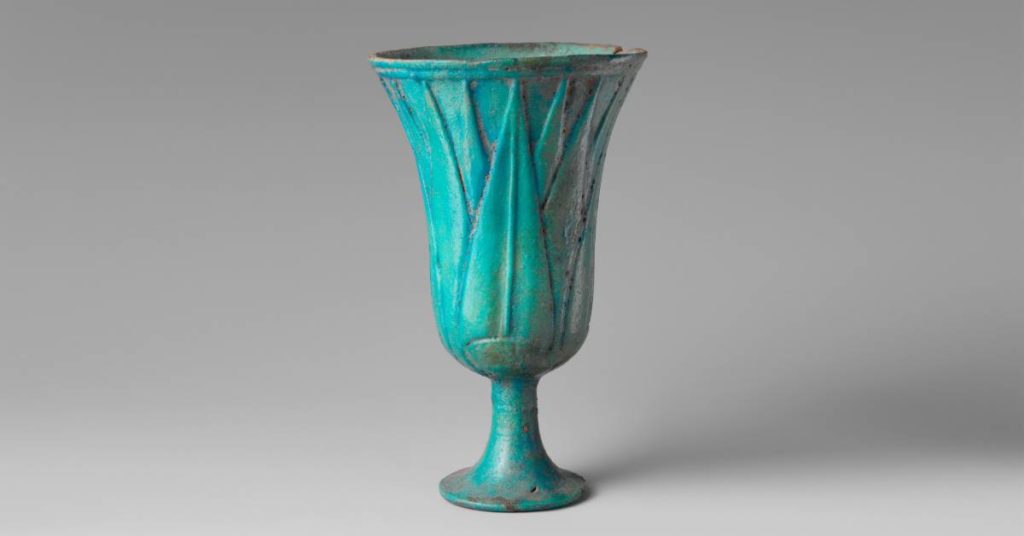

In the modern-day pottery studio, you’ll hear this technique referred to as overglaze decoration, overglaze enamels, or enameling.
Egyptian relief carving
Egyptian relief carving is a way of decorating pottery. The two kinds of relief carving are low and high. Low relief displays the design by cutting into the surface of the clay. High relief carvings were raised designs that stood off the pot.
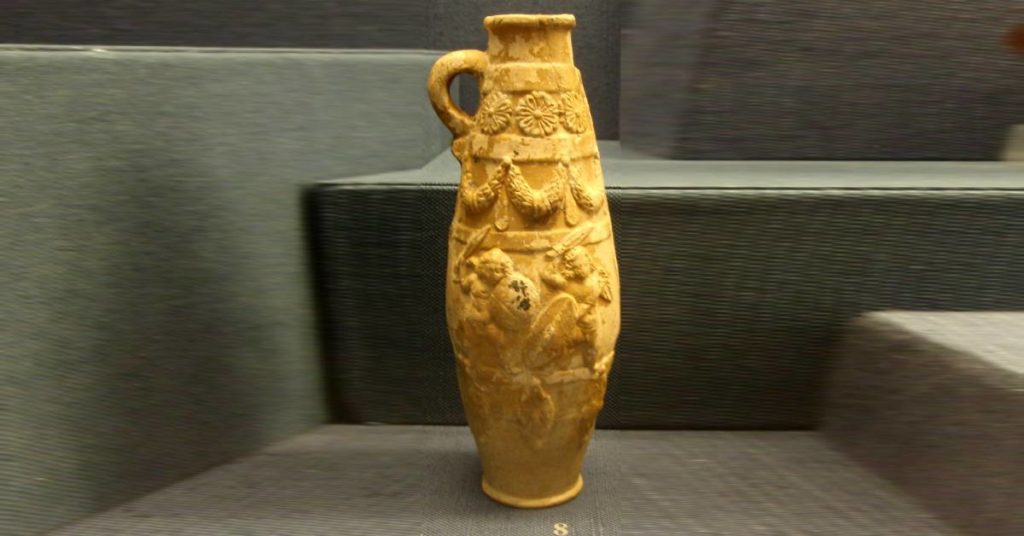

Eygpt Faience
We talked earlier about how all of Egyptian pottery is sometimes called “Faience”. But it’s actually a style employed by ancient Egyptian potters used to show animal or human figures.
Faience comes from the type of clay used. It is efflorescence glazing (or self-glazing) where salts come to the surface as a clay body drys. A glaze naturally develops when the vessel is fired. Egyptian faience results in bright colors like turquoise or cobalt blue.

Conclusion
The ancient Egyptian culture may have been the most influential human civilization ever. And Egyptian pottery is a big part of what lives on and tells the Egyptian story. I hope you enjoyed learning a bit of history and how/what pottery was made in ancient Egyptian times.
If you have any questions or comments, please email us at hello@wheelandclay.com. We’d love to hear from you!







