we’ve talked about this… I am a pretty big history nerd. And there’s a significant marriage between art and the past. Which means I get to write about two of my loves – art and history – on this blog!
In this article, we’ll take a look at some of the main ancient pottery cultures that have shaped the traditions you see in museums or in your cabinets.
Author's note: I know this isn't a comprehensive list of ancient pottery cultures. What you'll see in this article detail the cultures I've taken a deep dive into. We'll be updating it as we do our own research so be sure to check back here in the weeks to come as we write more!
Pottery cultures from the Americas
Mayan pottery
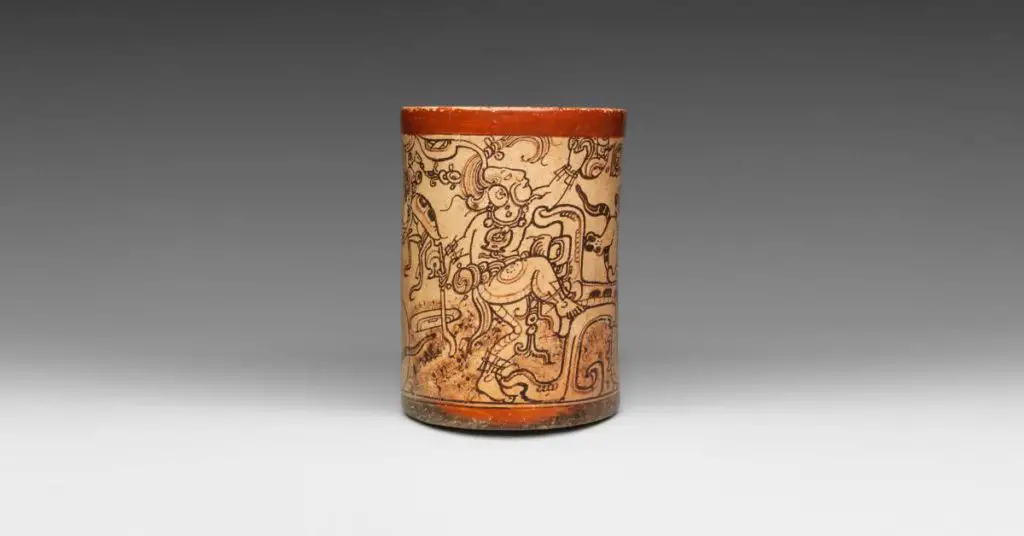

The earliest settlements of the ancient Mayans date around 1800 B.C. Early Maya was an agrarian culture. And the fertile Yucatan Peninsula in Central America aided the Mayans in becoming a powerhouse for the next 3,000 years in ancient Mesoamerica. Pottery fragments date the earliest ceramics from the Mayan people around 900 B.C.
Palenque is one of the archaeological sites that historians have taken to calling the art capital of the Mayan empire since advanced artworks have been discovered in the ruins of the city. Unlike other powerful empires, Palenque doesn’t appear to be a uniquely rich or big city. But even the city’s structures boasted art with stucco sculpture (perfected in the Early Classic Period) and carvings with high reliefs.
Polychrome pottery is what Mayan potters are most famous for. The decoration technique uses 3 or more mineral slips of varying colors. The different colors give the potter opportunities to add depth or contrast to their designs.
Read our article “A guide to ancient Mayan pottery” for more on this fascinating ancient culture.
Navajo pottery
The Athapaskans are a group of tribes now found in Alaska and northern Canada. A portion of those people migrated to the modern Navajo Nation and now make up the Navajo people. The first Navajo pottery recorded was made between 1500 – 1700 AD.
One of those popular styles from the Navajo people is called etched pottery. The bright color and intricate designs demonstrated in the pictured piece have become synonymous with Navajo pottery. The piece was poured from a mold. The potter then uses a wheel to paint the piece. That’s how the paint is added around the edges in bands. The artist’s hand etches a design into the surface and the pot is fired.
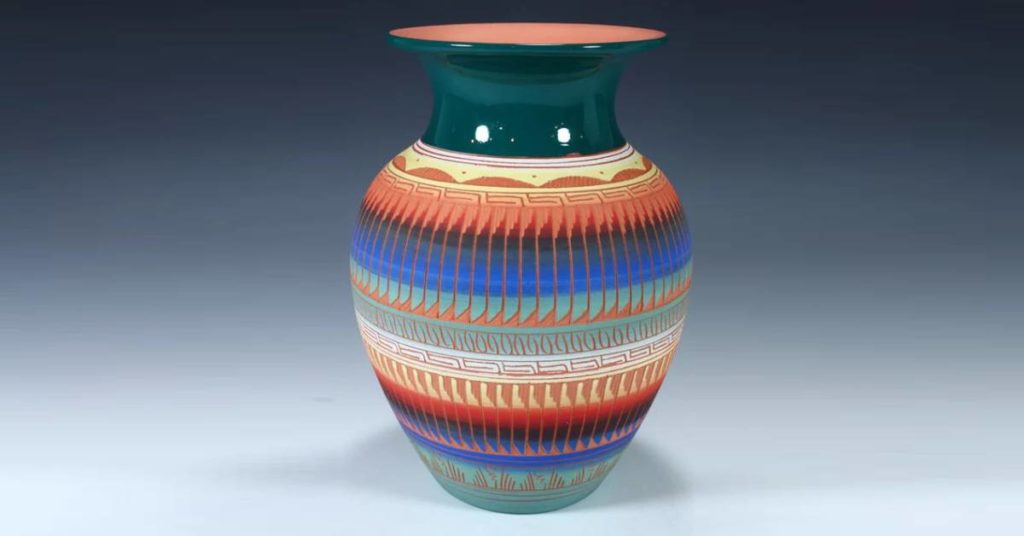

Check out “9 Navajo pottery designs you’ll want to check out” at the link to see some incredible styles from the Navajo people.
Pueblo pottery
Pueblo pottery has been dated back as early as 200 AD. The Puebloans settled in modern-day New Mexico, Northern Arizona, and other parts of the Southwest United States. They are known widely in the art community for their craftsman-level pottery. Archeologists believe the first Pueblo people to settle in these regions did so around A.D. 100 or 2,000 years ago.
Acoma pottery is a popular pueblo polychrome style. Acoma pottery is known for intricate geometric patterns and black and orange colors on the clay pot.
Check out our article “A guide to ancestral Pueblo pottery” for more on this culture and their pottery.
Aztec pottery
The first recorded people to settle in modern-day Mexico happened about 1500 years ago. It wasn’t for another 500 years that the Mexica people settled in this area.
Two popular styles from the Aztec’s are redware and whiteware. The technique is the same, but the clay body is what makes it different. The potter would use mineral and natural pigments to paint a finish onto the clay. After firing, the potter would etch geometric designs, landscapes, or human figures into the piece. This etching revealed the natural clay background.
Read our article “A guide to ancient Aztec pottery” to learn more.
Mediterranean pottery cultures
Greek pottery
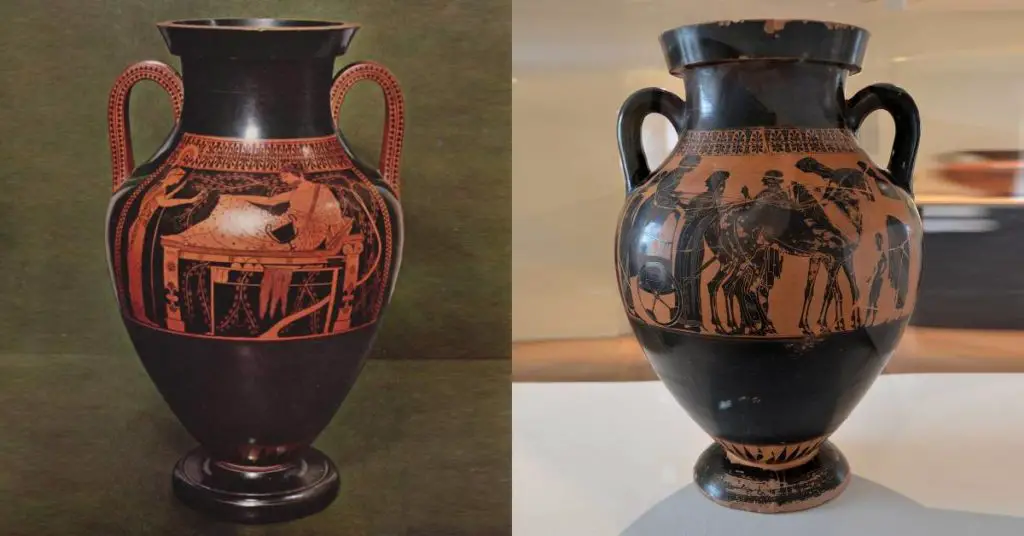

The earliest known pottery pieces from ancient Greece are dated somewhere between 7,000 – 3,500 B.C. These pieces were discovered along Greece’s eastern shoreline is along the Aegean sea. Many ancient Greek pieces are named according to this body of water. So when you’re looking up ancient Greek pottery you’ll likely see the word “Aegean”. Regions across Greece sprang up as art and culture hubs. Ultimately, the introduction of the potter’s wheel made the Peloponnese region a pottery production hub.
The Greeks had 13 various forms and styles of pottery vessels. Each shape had a defined purpose from storage jars for olive oil to use in religious ceremonies. We have a table at this link with a description and diagram of the pottery shapes.
In later years, the predominant styles made by ancient Greeks came to be geometric designs (what many people think of when they think of Ancient Greek pottery).
Read our article “A guide to ancient Greek pottery” to learn more.
Egyptian pottery
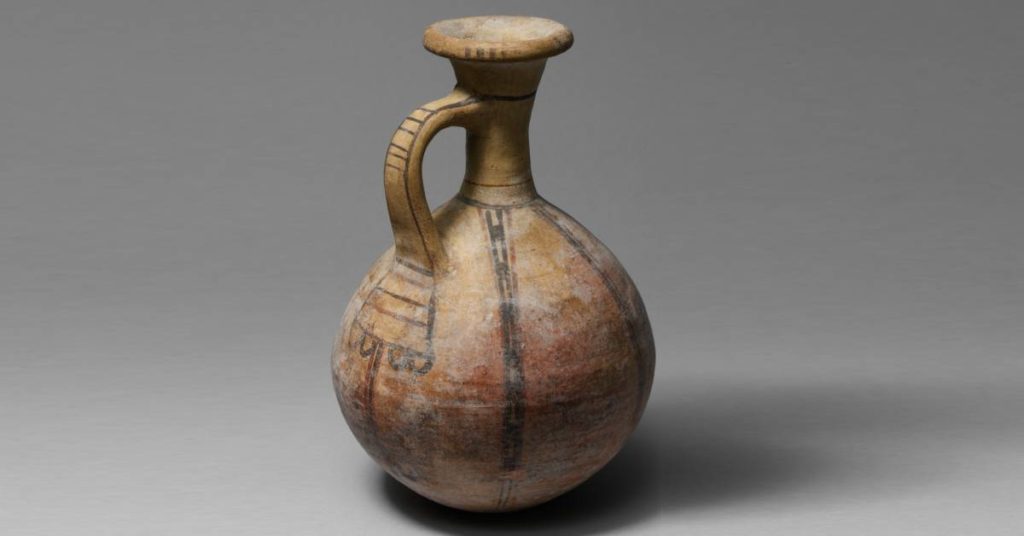

Egyptians started making pottery around 4,000 B.C.E. This dates Egyptian pottery earlier than the Old Kingdom (when Egyptian historians started making records). That’s a long time ago!
Egyptian potters pioneered the technology for making an ancient pottery vessel like new firing processes with kilns, the pottery wheel, and different types of glazes.
You may see “Egyptian faience” when looking up things about ancient Egyptian pottery. Faience is efflorescence glazing (or self-glazing). Salts in the clay material come to the surface as a clay body drys. A glaze naturally develops when the vessel is fired. Egyptian faience results in bright colors like turquoise or cobalt blue.
Read our article “A guide to ancient Egyptian pottery” to learn more.
Eastern pottery cultures
Japanese pottery
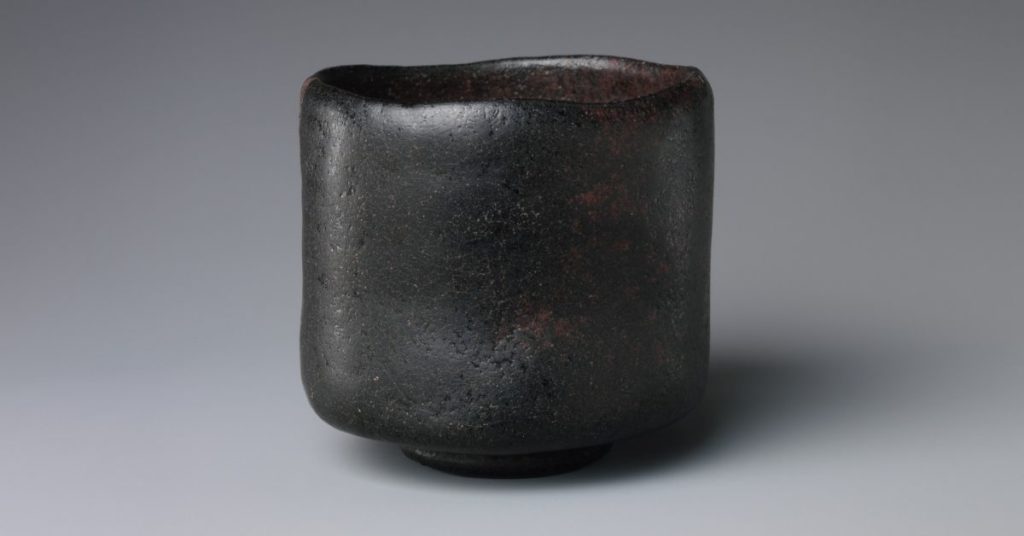

The earliest discovered pieces come from the Jōmon period (14,500 – 300 BCE). Pottery from this time lacked glaze and was baked in large fires. Many of the pieces were functional. Yet, pottery from this period was far from primitive.
Japan has 5 primary ceramic types that were determined by the district, ceramic materials used, and the way the pieces were fired. One of the best-known creative inventions is called kintsugi or “golden joinery”.
Read our article “A Guide To Japanese Pottery” to learn more.
What is the oldest form of pottery?
Some of the earliest recorded pieces of pottery are found in East Asia. But the first culture of pottery making that demonstrated aptitude and discipline was found in Japan. This grouping of ceramic vessels is now referred to as Japanese Jomon pottery (Japan’s neolithic period).
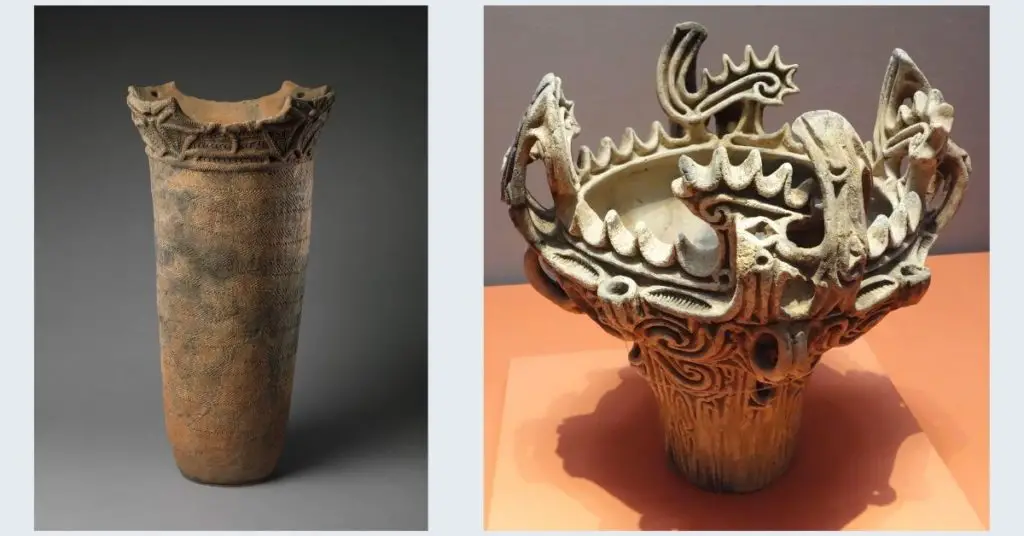

The earliest discovered pieces come from the Jōmon period (14,500 – 300 BCE). Pottery from this time lacked glaze and was baked in large fires. Many of the pieces were functional. Yet, pottery from this period was far from primitive.
What was pottery used for in ancient times?
Similar to now, pottery in ancient times had utilitarian purposes. The most common items were bowls, vases, and plates for storing foods and liquids, carrying items, and serving at meal times.
Many ancient cultures were deeply spiritual and some of the oldest pottery found was intended for ceremonies and rituals. In ancient Egypt, a particular vessel would be filled with oils and fragrant liquids and then buried with royalty. The Egyptians also made human forms that represented different deities. The Mayans would catch the blood from ritualistic sacrifices in specific ceramic pieces. The blood would then be offered to their deities for good results in war, favorable seasons, or fertility.
What pottery tools did the ancient potter use?
All cultures started with handbuilding techniques. Then they moved to simple tools that helped carve specific shapes and designs. The ancient Japanese pottery started using sophisticated kilns at a surprisingly early timeframe.
One unifying feature of all the cultures we’ve described today is that once the potter’s wheel was introduced, mass production became feasible and ceramic wares became commonplace.
Ancient pottery designs
We’ve touched on a handful of these when discussing the different cultures. I expect you’ll recognize some of these designs from a textbook or your own research since they are the forms and designs that have held humans’ attention for the longest.
Kintsugi

Kintsugi is an art form of rejoining a broken pottery piece with a lacquer mixed with powdered gold or other metals as the adhesive.
You may have heard of Kintsugi referred to as Japanese pottery gold or Japanese broken pottery. That’ because kintsugi means “golden joinery”. And is sometimes referred to as kintsukuroi meaning “golden repair”.
Check out our article “What is kintsugi?” to learn more.
Black figure pottery
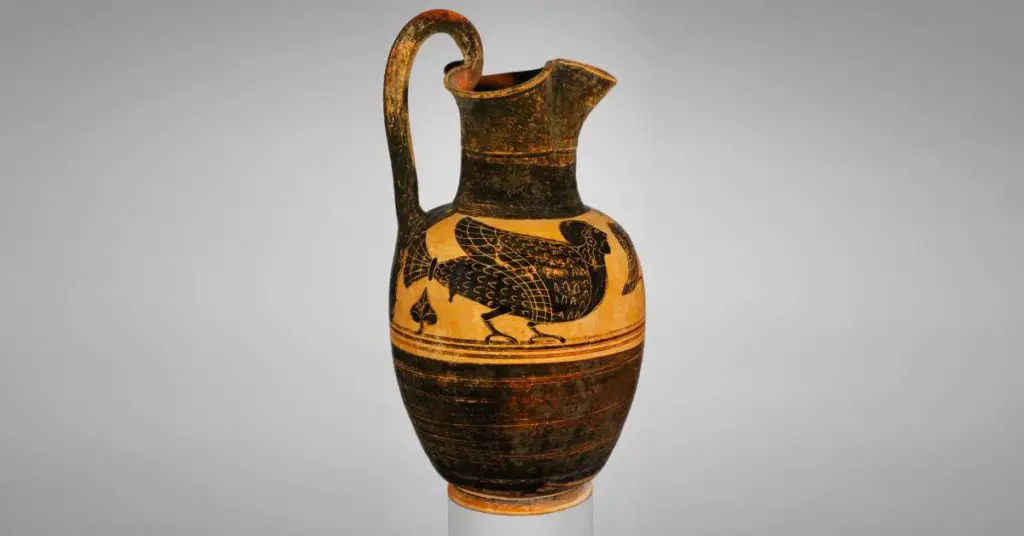

Black-figure pottery is a technique used in Ancient Greek ceramics. Slip and natural substances are added to the face of the pot. A potter then paints and draws designs on the surface of a vessel during the leather hard stage of clay. The parts that have slip blacken during kiln firing giving the technique its name.
Read our article “How the Ancient Greeks made black-figure pottery” to learn more.
Red figure pottery
The red-figure pottery painting style is an ol’ switcharoo from the black-figure pottery. An artist would paint designs and figures in red on a black background.
A few decades after black-figure painting took Greece by storm, the red-figure style replaced it. The red-figure style was popular domestically and internationally. Archeologists have discovered red-figure pots from Greece in Italy and even further north into Europe.
Sgraffito
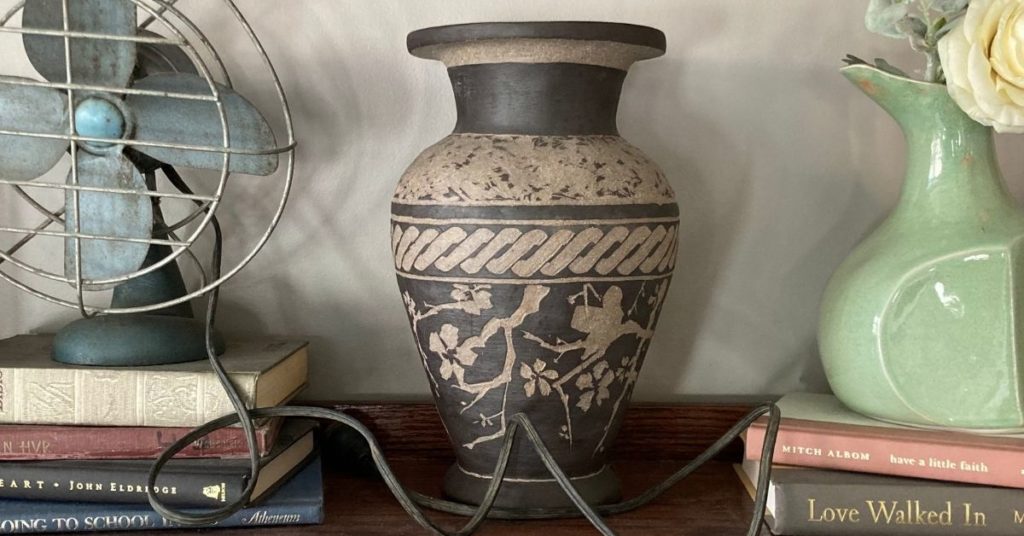

Sgraffito is a ceramic decoration technique. A potter paints engobe, underglaze, or slip onto the surface of a leather hard vessel. Then carves away the decorative material creating patterns, a design, and contrast.
Sgraffito decoration originates from Italy in the 15th century. Sgraffito comes from the Italian word graffiare which translates as “to scratch”.
Sgraffito was a technique that came about during the Italian Renaissance. At first, it was a way of decorating walls and facades. Though popularized and solidified in Italy, there are sgraffito decorations from this time in Africa and the Middle East.
Read our article “What is sgraffito pottery?” to learn more.
Egyptian faience
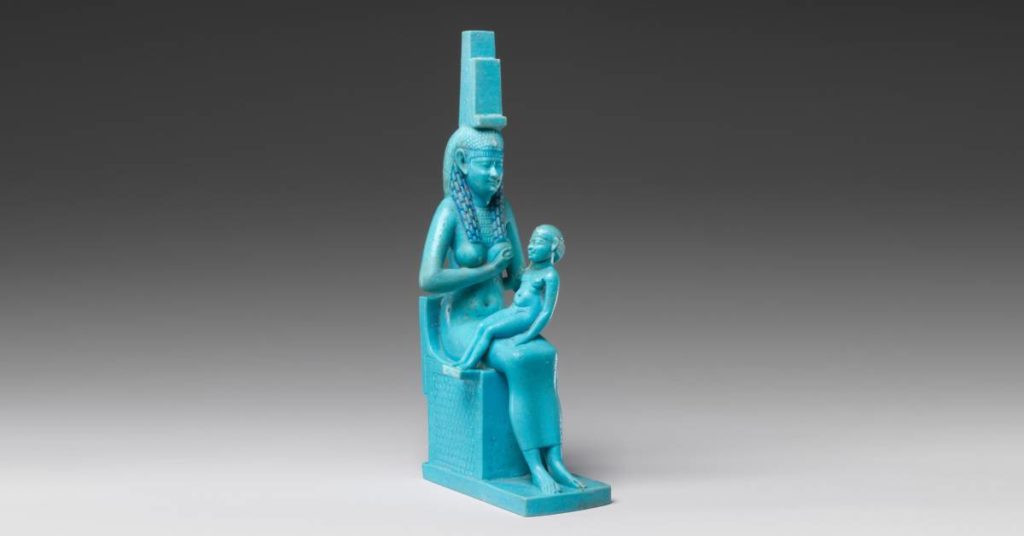

You may see “Egyptian faience” when looking up things about ancient Egyptian pottery. Faience is efflorescence glazing (or self-glazing). Salts in the clay material come to the surface as a clay body drys. A glaze naturally develops when the vessel is fired. Egyptian faience results in bright colors like turquoise or cobalt blue.
Conclusion
So many beautiful and storied pottery cultural traditions have shaped what we cherish today in the art world. And you can thank these ancient potters for their innovation in techniques, fire processes, and technology.
If you have any questions or comments, please email us at hello@wheelandclay.com. We’d love to hear from you!







